Keeping systems safe is the top priority of any organization as many malicious activities can be performed on data, networks, or the entire system environment for various reasons. Security providers are also using different approaches to keep the data and network security robust.
To keep network and data secure, developers have come up with the Zero Trust Security Framework.
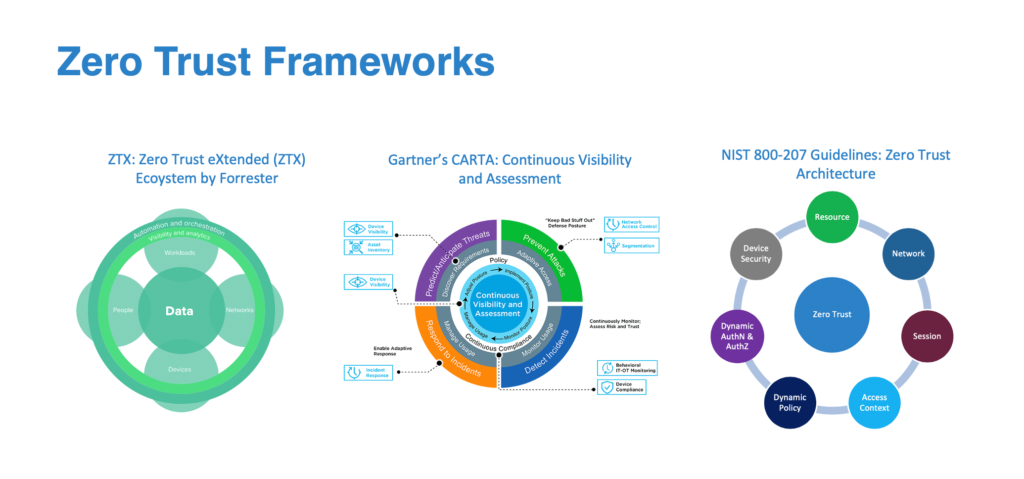
What is Zero Trust Security Framework?
The term Zero Trust was coined by John Kindervag n 1995 with the approach “never trust, always verify”. It continuously validates the interaction and enforces policies to validate the context of the request including the user’s ID, location, device used, and the request made. It works on the approach of never trusting any request, implicit or explicit.
Establishing a Zero Trust Architecture calls for strong multifactor authentication (MFA) methods beyond passwords, such as biometrics or one-time codes, as well as visibility and control over the environment’s users and traffic, including encrypted traffic.
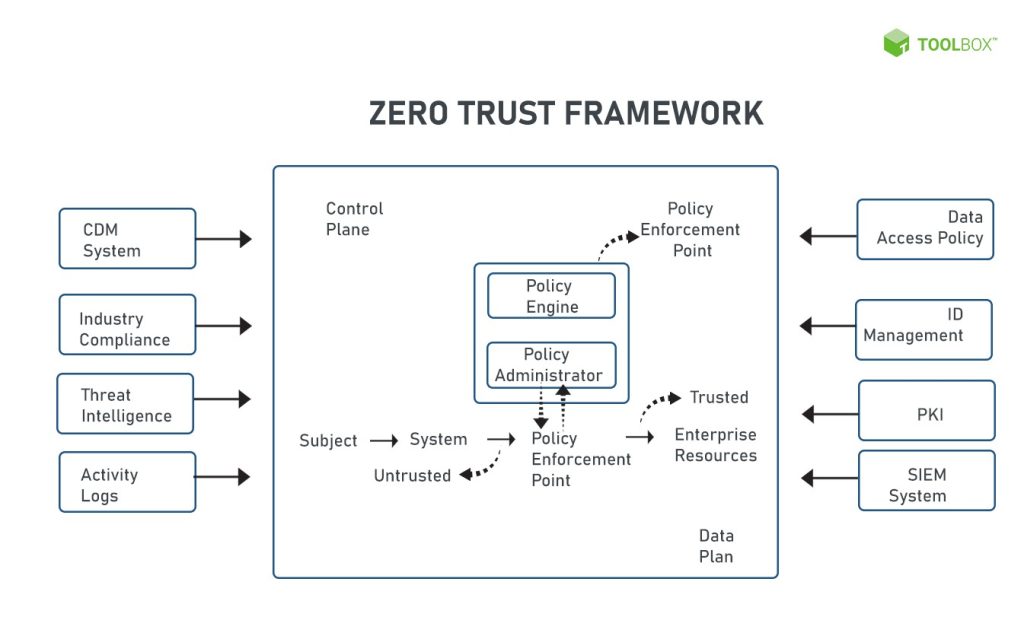
How does the Zero Trust Model work?
Zero Trust Architecture simply assures every action or request is malicious and can be detrimental and hence makes data and network inaccessible by default. It treats not only explicit but also implicit or known requests as harmful and hence verifies every request through different practices. For instance, the communication of workloads is stopped until the identity is validated by fingerprints, biometrics, or any other medium.
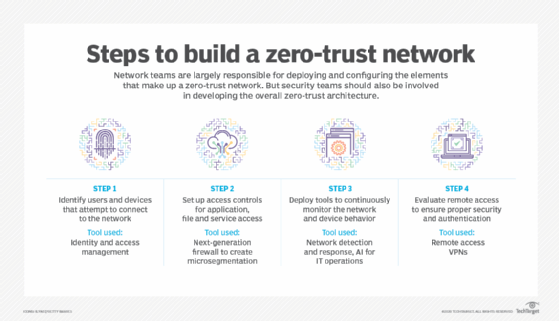
Core principals of Zero Trust
The core principles on which the zero trust security model works are:
Terminate every connection
Unlike the traditional approach, the Zero Trust approach terminates all the connections and verifies them before proceeding. It inspects all traffic including the encrypted ones to prevent any ransomware, malware, or other security threats from reaching the destination.
Context-based approach
It uses context to verify the user’s request including identity, location, request type, and device by which the request is being sent.
Reduce risk by eliminating the attack surface
Direct connections between users and apps reduce the possibility of lateral movement and stop compromised devices from infecting other resources. Additionally, users and apps cannot be found or attacked since they are invisible to the internet.
Benefits of using Zero Trust
Better Monitoring of Events
Zero trust security tools use various event analyzers to log and analyze events. It helps to predict the possible security threats against data through any suspicious activity and alerts the authorized stakeholders to remediation.
SSO Deployment
One of the benefits of Zero Trust security architecture is the need to deploy a single-sign-on system which eliminates the need for different passwords for different accounts. It improves the user experience.
Infrastructure Account Inventory
Zero trust architecture requires to have accurate monitoring of the devices, users, data, applications, and services being used in the infrastructure to verify the request. This accurate monitoring of inventory helps to manage operations in several ways.
Centralized security
Unlike traditional security architecture, the Zero Trust framework allows you to manage all aspects of the organization in a centralized form. This prevents any part from being vulnerable and streamlines the security monitoring for the stakeholders.
Easily relocate applications
Organizations need to relocate the application for various reasons. Having a centralized security architecture saves the time for employees to recreate security policies at the new location as the security policies from the centralized system can be deployed on the application at the new location easily.
Final Words
Deploying Zero Trust Security Architecture helps you validate users every time a request is made and this prevents unauthorized users to access the data. Deploying Zero trust Architecture has a great ROI as any malicious attack like ransomware asks for a bigger amount than deploying and managing the Zero Trust Architecture. Many organizations provide tools and help you deploy Zero Trust Security Architecture in your organization for a better and centralized security architecture.
FAQs
-
How to implement zero trust security ?
The following zero trust guidelines can help you design and deploy your zero trust cybersecurity framework. Define the protect surface. Working tirelessly to reduce the attack surface is not viable in today's evolving threat landscape. Map the transaction flows. Architect a Zero Trust network. Create the Zero Trust policy. Monitor and maintain the network.
-
What is encrypted traffic in network ?
Encrypted Traffic Analysis is a method of malware detection and cryptographic assessment of secured network sessions, which does not rely on decryption. This improves visibility of encrypted traffic
-
What is threat in cyber security ?
Cybersecurity threats are acts performed by individuals with harmful intent, whose goal is to steal data, cause damage to or disrupt computing systems.
-
What is a Zero Trust Architecture ?
Zero Trust is a strategic approach to cybersecurity that secures an organization by eliminating implicit trust and continuously validating every stage of a digital interaction.