Introduction
Industries have been evolving digitally and this metamorphosis in the working of different industries has evolved many new technologies. These technologies are useful to thrive in the industrial competition and achieve targeted goals. From automating tasks to using Artificial Intelligence to replicate human-like decision-making capabilities, technology has transformed the way industries work these days. One of the many such technologies that are being deployed by leading industries is Robotic Process Automation (RPA).
RPA automation is a great way to automate mundane and repetitive tasks to reduce human efforts and shift human resources to better use.
What is Robotic Process Automation?
Robotic Process Automation is a technology based on intelligent automation that automates high-volume, repetitive tasks by mimicking human interactions. These tasks can include logging in to a computer, copy-pasting specific files, updating employee information, time-sheet submission, etc. The robotic process automation tools build “robots” or “bots” to complete tasks without the need for human interference.
The RPA bots are provided with a set of instructions to perform ”if, then, else” statements on unstructured data. These bots then mimic human interactions and perform repetitive tasks automatically to let employees focus on tasks with higher value and must need human intelligence.
By integrating RPA automation with AI and ML, the bots can learn to perform tasks through the information given in various ways including text, images, and videos. It can read a text and fill out forms using OCR or can analyze images to provide image insights.
How does Robotic Process Automation Work?

Operating RPA involves carrying out a number of workflow operations. The software bots are given instructions on what to do at each level. Once this workflow has been programmed into the RPA, the program can then be automatically executed by the software, doing the required task repeatedly as needed. RPA replicates how users are used to interacting with and contemplating software programs. RPA’s approach is the ability to mimic how humans carry out computer-based processes, as opposed to automation techniques like application programming interfaces (APIs) or low-code development that are more scalable but less user-friendly or demand specialized knowledge.
RPA automation is a great way to automate mundane and repetitive tasks to reduce human efforts and shift human resources to better use.
How to Deploy RPA?
Deploying RPA needs to strategize the entire process effectively. RPA is not a physical entity but a software bot that requires to be integrated well with your current tools to show effective outputs. The four phases of implementing RPA methodology in your organization are Planning, Development, Testing, and Support and Maintenance.
Planning
This phase involves analysis requirements, planning automation, and recognizing future requirements of the organization with respect to automation and technology and its impact on the current deployment.
Development
This phase includes the actual development of bots according to the outputs of the planning phase. RPA developer chooses RPA tools that suit best the requirements, and working on them to build the bot comes under this phase.
Testing
This phase involves testing the created robot on real-world tasks to check its efficiency.
Support and Maintenance
It includes after-care and maintenance of the bot to keep it seamless with the ever-changing needs of the organization.
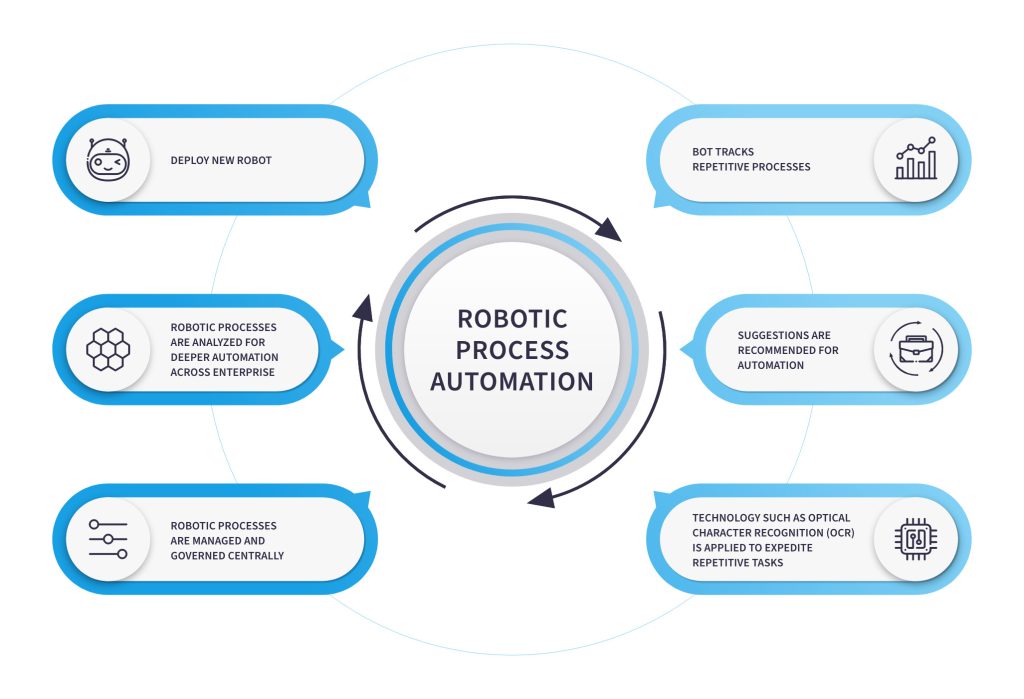
How RPA is impacting different industries?
Many industries are benefiting by including RPA in their systems. Some Robotics Process Automation applications for different industries are-
Healthcare
Medical Organizations deploy RPA to maintain patients record, billing, account management, schedule appointments, discharge procedures, and monitor patients remotely.
Finance and Banking
Robotic Process Automation in banking and finance can automate tasks like account opening and closing, foreign exchange, managing audits, loan processing, salary uploads, interest calculations, etc.
Customer Service
Many customer services include verification, managing refunds, processing queries, uploading documents, and approving or rejecting applications.
Accounting
The accounting sector can use RPA in vendor verification, purchase order entity, invoice processing, cross-cheking invoices, extracting data, and much more.
Supply Chain Management
Supply chain management can use RPA in monitoring and managing inventory, processing payments, tracking shipments, predicting delays and downtimes, etc.
eCommerce
eCommerce stores can use RPA to manage inventory, predict sellouts, manage billing and returns, track shipments and delays, product categorization, etc.
Human Resource
In human resources, RPA can manage job applications, new hiring and onboardings, sending offer letters, scheduling interviews, and sending auto-generated replies to the candidates with positive or negative feedback.
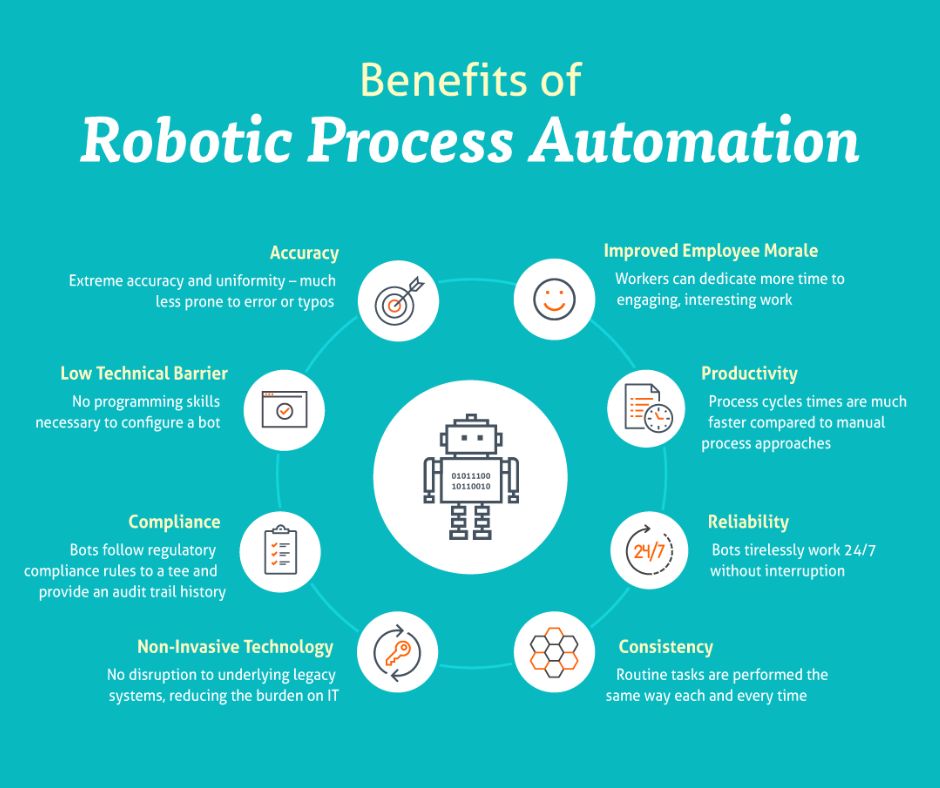
Benefits of RPA
Organizations can save employment costs and human error by deploying RPA. Kofax, an expert in intelligent automation, says the basic idea is straightforward: Let human employees work on what humans excel at while using robots to handle tasks that get in the way. Bots often don’t require specialized software or extensive system integration, making them inexpensive and simple to create. These qualities are essential as firms strive for expansion without increasing major costs or employee conflict.
According to Kofax, bots can increase the efficiency of organizations by 35%-50% if deployed correctly. By integrating RPA with cognitive technologies like Artificial intelligence and machine learning, organizations can maximize the effectiveness of technologies.
Limitations of RPA
Like with every other technology, RPA also has its limitations. The challenges RPA has to face are-
Security
RPA may need to access information to perform a task. It can be a significant risk to data security.
Limited Capabilities
RPA has limited capabilities as it only automates a task. Organizations often need to work on an entire process which includes performing more than one task. RPA shows massive limitations in capabilities in such processes.
Scalability
Although building RPA is easier than any other technology, scalability is a significant issue with RPA models.
Efficiency
RPA shows limited efficiency compared to many other technologies available such as automating processes through APIs.
Future of RPA software
The future of RPA lies in integrating RPA with artificial intelligence. The current limitation of RPA is to process small tasks that the bot learns with give instructions. By implementing AI in RPA, the bots will be able to analyze data and take decisions according to that data. The bots will also be able to initiate the process, make necessary decisions and run the entire process without human intelligence. Process automation and the cognitive capability of RPA will help organizations deal with complex tasks seamlessly.
RPA in the future will be able to handle tasks that are less routine-based and need smarter decision-making capabilities.
Conclusion
Robotic Process Automation can assist businesses to achieve mundane tasks efficiently and accurately but it still lacks the intelligence to perform the decision-based processes. The rapid growth in the deployment of RPA in industries like healthcare, finance, banking, eCommerce, etc can motivate technophiles to build bots that are smarter and self-sufficient to make correct decisions. The robots created through Robotic Process Automation tools have limited capabilities but are easier to build, and deploy and hence are being accepted by organizations to work efficiently and improve organizations’ overall productivity.
FAQs
-
What is robotic process automation ?
Robotic process automation (RPA) is a software technology that makes it easy to build, deploy, and manage software robots that emulate humans actions interacting with digital systems and software.
-
How rpa is deployed on cloud ?
Cloud RPA enables users to automate any process via a web-based interface accessed in their browser. A real cloud-native RPA platform means engineering the design, implementation, deployment, and operation of the application as a cloud technology.
-
Why rpa is important in modern business ?
RPA help cut back human capital costs as you scale, but it can also help avoid the consequences of human error. In addition to the money RPA can help you save, it can also free up a lot of your existing employees time, allowing them to focus on value-added tasks such as business development.
-
What is the future of rpa ?
The future of RPA is integrated, intelligent and intuitive. Automation and the technology that facilitates it move quickly. Variously known as intelligent automation, intelligent process automation and cognitive RPA, this class of solutions enables enterprises to automate more complex, less rule-based tasks.